연구용
Phospho-MARCKS (Ser158) Antibody [D19L10]
카탈로그 번호: F2837
적용:
반응성:
사용 정보
| 희석 |
|---|
|
| 응용 |
|---|
| WB |
| 반응성 |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| 출처 |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| 보관 완충액 |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| 보관 (수령일로부터) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
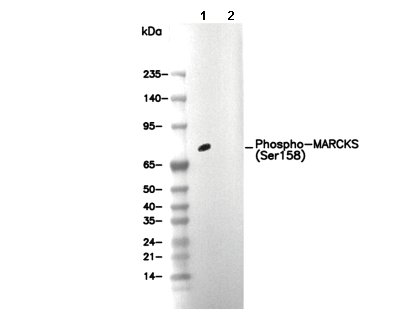
| 예측 분자량 관찰 분자량 |
|---|
| 32 kDa 87 kDa |
| *예측 분자량과 실제 분자량이 다른 이유는 무엇입니까? 다음과 같은 이유로 예측 분자량과 실제 단백질 분자량 간에 차이가 있을 수 있습니다. |
| 양성 대조군 | Mouse brain; Rat brain; HEK293; Hela (treated with TPA at 10 µg) |
|---|---|
| 음성 대조군 |
실험 방법
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 60 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution ( recommending 5% BSA solution)
for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
생물학적 설명
| 특이성 |
|---|
Phospho-MARCKS (Ser158) Antibody [D19L10] detects endogenous levels of MARCKS only when phosphorylated at serine 158. |
| 세포 내 위치 |
|---|
| Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton, Membrane |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P29966 |
| 클론 |
|---|
| D19L10 |
| 동의어 |
|---|
| MACS, PRKCSL, MARCKS, Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate, 80K-L protein, PKCSL |
| 배경 |
|---|
| MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate) is a ubiquitously expressed, evolutionarily conserved, natively unfolded protein and a major substrate of conventional and novel PKC isoforms. Structurally, it contains three conserved domains: an N-terminal myristoylation site (for membrane anchoring), a central lysine-rich effector domain (ED; aa 151–175) that binds actin, Ca²⁺/calmodulin, and PIP₂, and the MH2 domain of unknown function. MARCKS associates with the plasma membrane through both hydrophobic myristate insertion and electrostatic effector domain–PIP₂ interactions, a process regulated by the “myristoyl-electrostatic switch.” PKC-mediated phosphorylation of the effector domain (notably at serine 158). PMA significantly increased the phosphorylation of the MARCKS protein at serine 158, a site within its effector domain targeted by PKC, reflecting PKC-mediated regulation of MARCKS’ membrane association and actin-binding activity, causing MARCKS to translocate to the cytosol and modulate actin cytoskeleton reorganization, adhesion, migration, and exocytosis. Highly expressed in all eukaryotic cells (with MARCKSL1 enriched in brain, reproductive tissues, and macrophages), MARCKS is essential for embryonic development and neural functions. Its dysregulation contributes to inflammatory, allergic, and neoplastic airway diseases such as COPD, asthma, ARDS, and lung cancer, making it an important “druggable” target. |
| 참고문헌 |
|---|
|