P-glycoprotein (permeability glycoprotein, P-gp, Pgp, ABCB1, ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1, MDR1, and PGY1) is belongs to a subfamily of ABC-transporter called MDR (Classical multidrug resistance). P-glycoprotein functions as a transporter in the blood-brain barrier with a 170 kDa polypeptide. P-gp plays a role in the elimination of drugs and metabolites in kidney and liver, and these cumulative systemic effects would eventuate in lower plasma concentrations of these drugs. P-gp inhibitors can be a kind of anti-cancer drug through reducing multidrug resistance because P-glycoprotein (Pgp), the membrane-associated protein, is overexpressed in tumor cells resulting in an enhanced ability to export drugs from the cell and multidrug resistance.
P-gp
기타 Transmembrane Transporters 억제제
| Cat.No. | 제품명 | 정보 | 제품 사용 인용 | 제품 검증 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
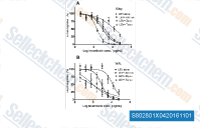
| S8028 | Tariquidar (XR9576) | Tariquidar는 CHrB30 세포주에서 P-glycoprotein의 강력하고 선택적인 비경쟁적 억제제로 Kd는 5.1 nM이며, MDR 세포주에서 약물 내성을 역전시킵니다. 3상. |
|
|
| S1481 | Zosuquidar 3HCl | Zosuquidar 3HCl은 세포 무첨가 분석에서 P-glycoprotein-매개 다제 내성의 강력한 조절제이며 Ki는 60 nM입니다. 3상. |
|

|
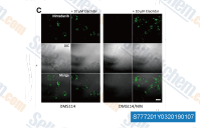
| S7772 | Elacridar (GF120918) | Elacridar (GF120918, GW120918, GG918, GW0918)는 강력한 P-gp (MDR-1) 및 BCRP 억제제입니다. |
|
|
| S4746 | (20S)-Protopanaxadiol | 진세노사이드의 주요 장내 대사산물인 (20S)-Protopanaxadiol (PPD, 20-Epiprotopanaxadiol)은 인삼의 활성 성분 중 하나입니다. (20S)-Protopanaxadiol은 다제내성 암세포에서 P-당단백질을 억제합니다. |
|
|
| S9145 | Solamargine | Solanum aculeastrum에서 분리된 생리활성 스테로이드 알칼로이드인 Solamargine은 강력하고 비선택적인 세포독성과 P-gp 억제를 유도합니다. |
|
|
| S3235 | Sinapine | Sinapine은 십자화과 식물 씨앗에서 분리된 알칼로이드로 항산화, 항종양 및 방사선 보호 활성을 가지고 있습니다. 이 화합물은 P-당단백질의 하향 조절을 통해 Caco-2 세포의 증식을 억제합니다. |
|
|
| S0921 | Wilforine | T. wilfordii 식물에서 발견되는 세스퀴테르펜 피리딘 알칼로이드인 Wilforine(WR)은 P-당단백질(P-gp)의 유출 활동을 유의하게 억제합니다. | ||
| S3431 | Encequidar (HM30181) | Encequidar (HM30181, HM30181A)은 아데노신 삼인산 결합 카세트 수송체 P-당단백질 (P-gp)의 강력하고 선택적인 억제제입니다. | ||
| E1781 | Biricodar | Biricodar(VX-710)는 생체 내 독성이 최소화된 P-glycoprotein 및 MRP-1 조절제입니다. 다양한 그람 양성 병원균에 대한 여러 항생제의 효과를 향상시키고, 다제 내성 세포에서 강력한 화학감수성 특성을 나타냅니다. | ||
| S8130New | Valspodar | Valspodar는 약물 유출을 차단하여 다제 내성을 역전시키는 2세대 비면역억제성 P-당단백질(Pgp) 억제제입니다. 이는 미톡산트론과 같은 화학요법제의 세포 내 축적을 향상시켜 내성 암세포의 약물 민감도를 회복시킵니다. | ||
