DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is a nuclear protein Serine (Ser)/Threonine (Thr) kinase that acts as both a molecular sensor and transmitter of DNA damage, and plays important roles in the DNA repair of double stranded breaks (DSBs), mediating immunoglobulin V(D)J gene recombination events, as well as telomere stabilization. [show the full text]
DNA-PK 억제제 (DNA-PK Inhibitors)
| Cat.No. | 제품명 | 정보 | 제품 사용 인용 | 제품 검증 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S8586 | Nedisertib (M3814) | Nedisertib (M3814, Peposertib, MSC2490484A)는 경구 생체 이용 가능하며, IC50 < 3 nM의 DNA activated protein kinase (DNA-PK)에 대한 고효능 및 선택적 억제제입니다. |
|
|
| S8843 | AZD7648 | AZD7648은 생화학 분석에서 0.6 nM의 IC50을 가지며 396개의 다른 키나아제에 대해 100배 이상 선택적인 DNA-PK의 강력한 억제제입니다. |
|
|
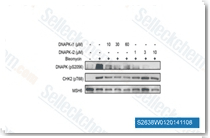
| S2638 | NU7441 (KU-57788) | NU7441 (KU-57788)은 IC50 14 nM의 매우 강력하고 선택적인 DNA-PK 억제제입니다. 또한 무세포 분석에서 IC50 1.7 μM 및 5 μM로 mTOR 및 PI3K를 억제하고, Cas9 매개 DNA 절단 후 NHEJ 빈도를 줄이는 동시에 HDR 속도를 증가시킵니다. |
|
|
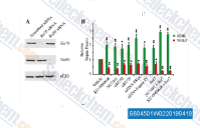
| S8045 | KU-0060648 | KU-0060648은 DNA-PK 및 PI3Kα, PI3Kβ, PI3Kδ의 이중 억제제로, 각각 8.6 nM 및 4 nM, 0.5 nM, 0.1 nM의 IC50을 가지며, PI3Kγ에 대한 억제는 0.59 μM의 IC50으로 더 적습니다. |
|
|
| S8593 | VX-984 | VX-984 (M9831)는 DNA-PK의 경구 활성, 강력하고 선택적이며 ATP 경쟁적 억제제입니다. 이 화합물은 비상동 말단 접합(NHEJ)을 효과적으로 억제하고 DNA 이중 가닥 파손(DSB)을 증가시킵니다. 이는 비소세포 폐암(NSCLC) 세포주를 포함한 다양한 암세포주에서 전리 방사선(IR)의 세포독성 효과를 시험관 내에서 향상시킵니다. 또한, 이 억제제는 DNA-PKcs 자가인산화를 감소시킵니다. | ||
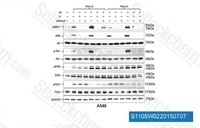
| S1105 | LY294002 | LY294002 (SF 1101, NSC 697286)는 각각 0.5 μM/0.57 μM/0.97 μM의 IC50으로 PI3Kα/δ/β를 억제하는 것으로 알려진 최초의 합성 분자이며, 워트마닌보다 용액에서 더 안정하고 자가포식체 형성을 차단합니다. 이는 Class I PI3K 및 기타 PI3K 관련 키나아제뿐만 아니라 PI3K 계열과 관련이 없어 보이는 새로운 표적에도 결합합니다. 이 화합물은 또한 98 nM의 IC50으로 CK2를 억제합니다. 이는 비특이적인 DNA-PKcs 억제제이며 autophagy 및 apoptosis를 활성화합니다. |
|
|
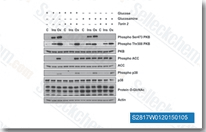
| S2817 | Torin 2 | Torin 2는 p53 / - MEF 세포주에서 IC50 0.25nM의 강력하고 선택적인 mTOR 억제제이며, PI3K보다 800배 높은 mTOR 선택성과 개선된 약동학적 특성을 가집니다. 이 화합물은 PC3 세포주에서 각각 EC50 28nM/35nM/118nM으로 ATM/ATR/DNA-PK를 억제합니다. 세포 생존력을 감소시키고 Autophagy와 Apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
|
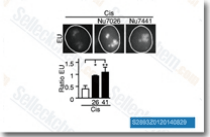
| S2893 | NU7026 | NU7026 (LY293646)은 세포 자유 분석에서 IC50이 0.23 μM인 강력한 DNA-PK 억제제이며, PI3K보다 DNA-PK에 대해 60배 선택적이며 ATM과 ATR 모두에 대해 비활성이다. 이 화합물은 G2/M 세포 주기 정지 및 세포자멸사를 강화한다. |
|
|
| S7891 | CC-115 | CC-115는 DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) 및 mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)의 이중 억제제로, IC50 값은 각각 0.013 μM 및 0.021 μM입니다. 잠재적인 항종양 활성을 가집니다. |
|
|
| S8379 | YU238259 | YU238259는 상동성 의존성 DNA 복구(HDR)의 새로운 억제제이지만, 세포 기반 GFP 리포터 분석에서 비상동성 말단 연결(NHEJ)을 억제하지 않습니다. |
|
|
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is composed of three key components including two DNA-binding subunits Ku70 and Ku80 (Ku86), as well as one DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs). Based on protein sequence similarity, DNA-PK belongs to the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) family, whereas, DNA-PK is not known to phosphorylate lipids and is therefore called PI3K-like kinase (PI3KK). The carboxyl-terminal region of Ku70 contains a SAP domain that is believed to be involved in chromosomal organization. The carboxyl-terminal region of Ku80 is required for the Ku70 and Ku80 heterodimer interaction with DNA-PKcs. The Ku heterodimer can bind to a variety of double-stranded end structures, including blunt ends, overhangs are the 3' or 5' end, and covalently closed hairpin ends. Like ATM and ATR, DNA-PKcs is structurally similar as it contains carboxyl-terminal domains, a large amino-terminal domain in addition to FAT and FATC domains flanking the kinase domain. The DNA-PKcs structure contains a channel large enough to accommodate double-stranded DNA, while the structure of Ku heterodimer is an asymmetric open ring, allowing the DNA to pass through the center. DNA-PKcs is one of the largest kinases identified to date, and it is the only kinase that is absolutely dependent on DNA binding for activity. DNA-PK has a strong preference for phosphorylating Serine (Ser) and Threonine (Thr) residues that are followed by glutamine or, less commonly, a hydrophobic residue. [1][2]
DNA-PK is involved in the ligation step of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway required for DNA double-stranded break (DSB) repair, V(D)J recombination and telomere stabilization. A heterodimer of Ku70 and Ku80 initially binds to the double-stranded DNA broken ends and translocates inwards in an ATP-independent manner and recruits DNA-PKcs. This results in the stabilization of the protein/DNA binding and enabling NHEJ to proceed. Moreover, DNA-PKcs acts as a scaffold protein by joining two broken DNA ends together in a complex containing two DNA-PKcs molecules that contributes to the synapsis of the broken DNA ends and the localization of DNA repair proteins such as DNA ligase IV/XRCC4 complex to the site of damage. DNA-PK is activated in cis by the DNA to which it is bound, and stimulated by Ku heterodimer as well as the interaction of two molecules of DNA-PKcs, while end-bridging through synapsis is required for full kinase activation. DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation at multiple sites, including Thr2609 and Ser2056, results in an inactivation of DNA-PK kinase activity and NHEJ ability. To ensure NHEJ can proceed efficiently, DNA-PK phosphorylates and activates the Werner syndrome protein (WRN) to remove 3' phosphate or 3' phosphoglycolate groups generated following IR, and the nuclease Artemis to remove 5' overhangs and shorten 3' overhangs. In addition, DNA-PK promotes processing of hairpin DNA structures in V(D)J recombination by activation of Artemis. Cells that lack DNA-PKcs are acutely radiosensitive and have defective DSB repair, while mice lacking DNA-PKcs remain viable but are immunodeficient (due to the absence of immune development) as a result of accumulated processed DNA intermediates. Additionally, DNA-PK has been strongly implicated in telomere maintenance. DNA-PKcs-/- mice display significant telomeric fusion events consistent with the role of DNA-PKcs in telomere maintenance. Furthermore, DNA-PK is involved in the modulation of transcription by phosphorylation of RNA polymerases including pol I and pol II through its kinase activity, thereby regulating the function of these enzymes. By direct p53 phosphorylation, the modification of Ku70 releasing Bax, or suppressing the expression of p21, DNA-PK plays a significant role in mediating a p53-dependent apoptotic response under a range of cellular conditions including exposure to ionizing radiation (IR), environmental carcinogens and chemotherapeutic agents or in cells that have critically shortened telomeres. [1][2]
Specific inhibitors of DNA-PK used to selectively reduce NHEJ activity have been shown to be effective as single-agent therapies in homologous recombination (HR) -defective tumors. Treatment with a flavone-based DNA-PK inhibitor IC87361 leads to tumor regression. The inhibitors of DNA-PK such as NU7441 enhance the cytotoxicity of physical and chemical agents, leading to reduced clonogenic survival and cellular proliferation, as well as increased apoptosis, regardless of p53 status. Moreover, DNA-PK inhibitors combined with other DNA-damage response (DDR) inhibitors enhance the therapeutic potential of anticancer agents. [3][4]
