AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular energy homeostasis as the principal energy sensor in most eukaryotic cells. In response to stress, AMPK activation switches on catabolic pathways that generate ATP while simultaneously inactivating biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP. [show the full text]
AMPK 활성제/억제제 (AMPK Activators/Inhibitors)
| Cat.No. | 제품명 | 정보 | 제품 사용 인용 | 제품 검증 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S7306 | Dorsomorphin Dihydrochloride | Dorsomorphin 2HCl은 세포 유리 분석에서 Ki가 109 nM인 강력하고 가역적이며 선택적인 AMPK 억제제로, ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA, JAK3를 포함한 여러 구조적으로 관련된 키나아제에 대한 유의미한 억제를 보이지 않습니다. 또한 type Ⅰ BMP receptor 활성을 억제합니다. Dorsomorphin은 암 세포주에서 autophagy를 유도합니다. |
|
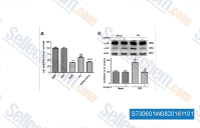
|
| S1208 | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Hydrochloride | Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl은 인간 DNA topoisomerase II를 2.67 μM의 IC50으로 억제하는 항생제입니다. Doxorubicin은 AMPK의 기저 인산화를 감소시킵니다. Doxorubicin은 HIV 감염 환자의 동시 치료에 사용되지만 HBV 재활성화 위험이 높은 것으로 나타났습니다.이 제품은 PBS 용액에 용해될 때 침전될 수 있습니다. 순수에 원액을 준비하고 순수 또는 생리 식염수로 희석하여 작업 용액을 얻는 것이 좋습니다.Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl은 신장 질환 동물 모델을 유도하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다. |
|
|
| S1950 | Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride (1,1-디메틸비구아니드 염산염)는 주로 간에서 포도당 신생(간에 의한 포도당 생산)을 억제하여 간세포의 고혈당을 감소시키는 매우 효과적인 혈당 강하제입니다. 또한 단핵 세포의 Mitophagy를 촉진하고 JNK/p38 MAPK 경로 및 GADD153 활성화를 통해 폐암 세포의 Apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
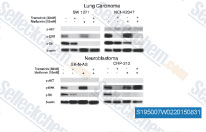
|
| S8161 | ON123300 | ON123300은 CDK4, Ark5/NUAK1, PDGFRβ, FGFR1, RET (c-RET), Fyn에 대해 각각 3.9 nM, 5 nM, 26 nM, 26 nM, 9.2 nM, 11 nM의 IC50을 갖는 강력하고 다중 표적 키나아제 억제제입니다. |
|
|
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol은 시클로옥시게나제(예: COX, IC50=1.1 μM), 리폭시게나제(LOX, IC50=2.7 μM), 키나제, 시르투인 및 기타 단백질을 포함한 광범위한 표적을 가지고 있습니다. 항암, 항염증, 혈당 강하 및 기타 유익한 심혈관 효과를 가집니다. Resveratrol은 mitophagy/autophagy 및 자가포식 의존성 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
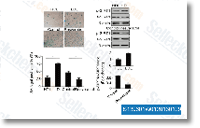
|
| S7840 | Dorsomorphin (Compound C) | Dorsomorphin은 세포 비활성 분석에서 Ki가 109 nM인 강력하고 가역적이며 선택적인 AMPK 억제제로, ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA 및 JAK3를 포함한 여러 구조적으로 관련된 키나제의 유의미한 억제를 보이지 않습니다. Dorsomorphin은 BMP type I receptors ALK2, ALK3 and ALK6을 선택적으로 억제합니다. Dorsomorphin은 특정 세포 분화를 촉진하고 암세포주의 자가포식을 유도하는 데 사용됩니다. 세포 테스트에는 수용성 S7306 Dorsomorphin (Compound C) 2HCl이 권장됩니다. |
|
|
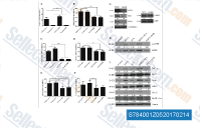
| S1802 | AICAR (Acadesine) | AMPK 활성제인 AICAR (Acadesine, NSC105823, AICA Riboside)는 ZMP 축적을 유도하며, 이는 AMP의 AMPK 및 AMPK 키나제에 대한 자극 효과를 모방합니다. 이 화합물은 mitophagy를 유도합니다. 3단계. |
|
|
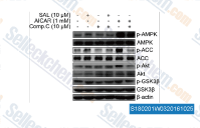
| S2697 | A-769662 | A-769662는 세포 유리 분석에서 EC50이 0.8 μM인 강력하고 가역적인 AMPK 활성제이며, GPPase/FBPase 활성에는 거의 영향을 미치지 않습니다. |
|
|
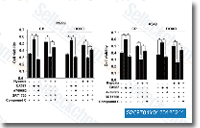
| S5958 | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide) | 제2형 당뇨병 치료에 널리 사용되는 약물인 Metformin (1,1-디메틸비구아니드)은 간세포에서 AMP-활성 단백질 키나아제 (AMPK)를 활성화시킵니다. Metformin은 단핵구에서 mitophagy를 촉진합니다. Metformin은 JNK/p38 MAPK 경로 및 GADD153 활성화를 통해 폐암 세포의 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
|
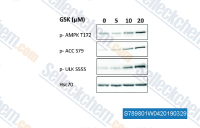
| S7898 | GSK621 | GSK621은 특이적이고 강력한 AMPK 활성제입니다. |
|
|
AMPK exists as a heterotrimeric protein complex composed of a catalytic α-subunit (α1 or α2) and regulatory β-subunit (β1 or β2) and γ- subunit (γ1, γ2 or γ3). The structure of the α-subunit consists of a conventional Ser/Thr kinase domain at the N-terminal, an auto-inhibitory domain (AID), an extended linker peptide and the α-subunit C-terminal domain (α-CTD). The β-subunit contains a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), with the β-subunit C-terminal domain (β-CTD) interacting with both the α-CTD and the amino terminus of the γ-subunit, thus forming the core of the complex. The γ-subunit includes four tandem repeats of a sequence motif, termed a CBS repeat (cystathionine β-synthase, CBS1-4), that forms a flattened disk with one repeat in each quadrant to create four potential ligand binding sites in the centre (site 1-4). AMPK activity increases more than 100-fold when the conserved Thr172 residue in the activation loop of the catalytic α-subunit is phosphorylated by upstream AMPK kinases (AMPKK) such as LKB1 requiring the change in AMP or ADP levels, and CaMKKβ (CaMKK2) in response to increases in cell Ca2+. AMP binding to ligand binding site 1 of the γ subunit allosterically activates the AMPK complex by facilitating the phosphorylation of Thr172 in the catalytic α-subunit, whereas binding of AMP or ADP to site 3 modulates the phosphorylation state of Thr172. In addition to allosteric activation by AMP, the effects on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Thr172 can also be produced by ADP, which requires N-terminal myristylation of the β-subunit. [1][2]
AMPK is activated by various types of metabolic stress (glucose deprivation, hypoxia, ischemia, metabolic poisons, or muscle contraction), as well as drugs and xenobiotics (metformin, resveratrol, or berberine) through the classical or canonical mechanisms, which involve increases in cellular AMP, ADP or Ca2+. The metformin for the treatment of people with type 2 diabetes indirectly activates AMPK by increasing cellular AMP and ADP, usually by inhibiting mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Additionally, AMPK activated by resveratrol or metformin upregulates genes involved in oxidative metabolism and oxidative stress resistance by regulating transcription factors of the abnormal dauer formation 16 (DAF-16)/forkhead box O (FOXO) family, contributing to its effects on extending healthy lifespan. Some types of cellular stress such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damaging agents (etoposide, doxorubicin and ionizing radiation) activate AMPK by non-canonical mechanisms that involve ATM rather than the increases in AMP, ADP or Ca2+ levels. Activation of AMPK enhances both the transcription and translocation of GLUT4, resulting in an increase in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. In LKB1-knockout but not AMPKα1-knockout mice, the effects of both AICAR and contraction on glucose uptake are lost. In addition, AMPK also stimulates other catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis via inhibition of ACC2 and activation of PFKFB. AMPK is also involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of PGC1α, and the turnover of mitochondria via the special form of autophagy termed mitophagy by activating ULK1, and subsequently triggering autophagy. In addition, mTOR complex-1 (TORC1) can be inhibited by AMPK mediated phosphorylation of both its upstream regulator, TSC2, and the TORC1 subunit Raptor. Consistent with its role in cellular energy homeostasis, AMPK also conserves ATP by switching off almost all anabolic pathways, including the biosynthesis of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and ribosomal RNA. Moreover, AMPK also functions beyond metabolism through regulation of the cell cycle and modulation of membrane excitability. As LKB1 is a tumor suppressor and is frequently mutated in spontaneous cancers, AMPK-activating drugs such as metformin or A-769662 significantly protect against the development of cancer. [1][2]
