IκBs are a family of related proteins that have an N-terminal regulatory domain, followed by six or more ankyrin repeats and a PEST domain near their C terminus. IκBα is the best-studied and major IκB protein. [show the full text]
IκB/IKK
| Cat.No. | 제품명 | 정보 | 제품 사용 인용 | 제품 검증 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S8922 | TBK1/IKKε-IN-5 | TBK1/IKK -IN-5 (화합물 1)는 TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) 및 I B kinase- (IKK /IKK-i)의 이중 억제제로, TBK1 및 IKK 에 대한 IC50 값은 각각 1.0 nM 및 5.6 nM입니다. TBK1/IKK 억제는 PD-1 차단에 대한 반응을 향상시키며, 이는 생체 내 종양 반응을 효과적으로 예측합니다. |
|
|
| S9042 | Wedelolactone | 약용 식물에서 유래한 천연 화합물인 Wedelolactone은 IκBα의 인산화 및 분해를 매개하여 NF-κB 활성화에 중요한 IKK의 억제제입니다. 이 화합물은 또한 caspase-11의 억제제입니다. |
|
|
| S8078 | Bardoxolone Methyl (RTA 402) | Bardoxolone Methyl (RTA 402, TP-155, NSC 713200, CDDO Methyl Ester, CDDO-Me)은 강력한 세포자멸사 촉진 및 항염증 활성을 나타내는 IKK 억제제이며, 강력한 Nrf2 활성제이자 핵인자-κB (NF-κB) 억제제입니다. Bardoxolone Methyl은 페로프토시스를 억제합니다. Bardoxolone Methyl은 암세포에서 세포자멸사 및 자가포식을 유도합니다. |
|
|
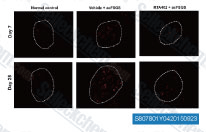
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol은 시클로옥시게나제(예: COX, IC50=1.1 μM), 리폭시게나제(LOX, IC50=2.7 μM), 키나제, 시르투인 및 기타 단백질을 포함한 광범위한 표적을 가지고 있습니다. 항암, 항염증, 혈당 강하 및 기타 유익한 심혈관 효과를 가집니다. Resveratrol은 mitophagy/autophagy 및 자가포식 의존성 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
|
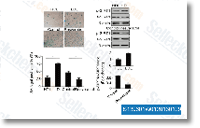
| S2882 | IKK-16 | IKK-16은 무세포 분석에서 각각 40 nM, 70 nM, 200 nM의 IC50을 갖는 IKK-2, IKK complex 및 IKK-1에 대한 선택적 IκB 키나아제(IKK) 억제제입니다. IKK-16은 또한 세포에서 LRRK2 Ser935 인산화를 억제하고 시험관 내에서 LRRK2 키나아제 활성을 50 nM의 IC50으로 억제합니다. |
|
|
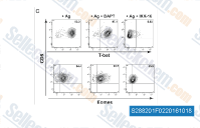
| S2824 | TPCA-1 | TPCA-1 (GW683965)은 세포 없는 분석에서 17.9 nM의 IC50을 갖는 IKK-2 억제제이며, NF-κB 경로를 억제하고 IKK-1에 비해 22배 선택성을 나타냅니다. TPCA-1은 또한 STAT3 억제제이며 Apoptosis를 향상시킵니다. |
|
|
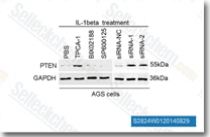
| S8044 | BMS-345541 | BMS-345541은 무세포 분석에서 IC50이 각각 0.3 μM 및 4 μM인 IKK-2 및 IKK-1의 촉매 서브유닛에 대한 고도로 선택적인 억제제입니다. |
|
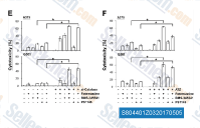
|
| S7352 | Bay 11-7085 | BAY 11-7085 (Bay 11-7083)는 TNFα 유도 IκBα 인산화를 억제하는 비가역적 억제제로, IC50 값은 10 μM입니다. |
|

|
| S2864 | IMD 0354 | IMD-0354 (IKK2 Inhibitor V)는 IKKβ 억제제이며 NF-κB 경로에서 IκBα 인산화를 차단합니다. |
|
|
| S7948 | MRT67307 HCl | MRT67307은 IC50이 각각 160 및 19 nM인 강력한 이중 IKKϵ 및 TBK1 억제제입니다. MRT67307은 ULK1 및 ULK2를 강력하게 억제하고 Autophagy를 차단합니다. |
|
|
IκB (Inhibitor of κB) functions as a primary inhibitor of NF-κB activation, with an N-terminal regulatory domain, followed by six or more ankyrin repeats and a PEST domain near their C terminus. [1] IκB family contains eight known members, IκBα, IκBβ, IκBε, Bcl-3 (B-cell lymphoma 3), IκBζ, and IκBns (NF-κBδ), as well as the precursor Rel proteins p100 (NF-κB2) and p105 (NF-κB1) due to the presence of multiple ankyrin repeats in their C-terminal halves. IκBα and IκBβ are broadly expressed in all type of cells, whereas IκBε is expressed only in hematopoietic cells. Bcl-3, IκBζ and IkBNS are atypical IκB proteins that exhibit limited expression following NF-κB activation. The regulation of IκB proteins varies by protein type, and each IκB moiety exhibits a unique affinity for NF-κB complexes. [2]
In unstimulated cells, the IκBα proteins mask the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-κB proteins, keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the cytoplasm. In response to stimuli, IκB kinase (IKK) phosphorylates IκBα leading to the degradation of IκBα, and subsequent NF-κB activation. IκBα expression can be activated by NF-κB to generate a negative feedback loop. Similar to IκBα, IκBβ acts by sequestering p65- and c-Rel-containing complexes in the cytoplasm. However, nuclear localized IκBβ also binds to p65:c-Rel heterodimers, promoting continued binding to specific κB sites, and augmenting late transcription of select target genes (i.e. TNF and IL-1β). IκBε is induced slowly, and selectively regulates p65 homodimers and c-Rel:p65 heterodimers. Bcl-3 functions as a transcriptional co-activator that may both inhibit and facilitate NF-κB-dependent transcription in a context-specific manner. Like Bcl-3, IκBζ can enhance transcription in association with p50 NF-κB dimmers despite the prescence of distinct mechanisms. IκBns selectively inhibits NF-κB-dependent pro-inflammatory gene expression by stabilizing p50 homodimers at κB sites. In addition to exclusively stabilizing RelB dimers, p100 itself can act more broadly in inhibiting NF-κB dimers. The p105 also acts like a typical IκB protein, and is additionally associated with the activation of the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway through the binding of MAP3K8 (TPL2). Moreover, the functions of individual IκB family members are quite heterogeneous and are not limited to this particular role in regulating NF-κB signaling. [2]
In oncology, the direct activation of NF-κB complexes through the loss of the inhibitory proteins IκBα and IκBε has been observed in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Since the NF-κB signal pathway plays a critical role in tumorigenesis bv way of abberant IκB activity, a variety of compounds targeting IKK and its associated enzymes are in clinical development. [3] For instance, the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (Velcade®) has been approved by the FDA for use in haematological malignancies. [4] In addition, Bortezomib is currently being explored in clinical development for its efficacy against solid tumors (clinicaltrials.gov; NCT00479128).
