Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR) is the receptor of VEGF. VEGFR is involved in cell proliferation, migration, survival and permeability. The VEGFs include five known structurally-related mammalian ligands (VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, and placenta growth factor, PLGF) and there are also three structurally related VEGFRs subtypes (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3). [show the full text]
VEGFR 억제제 (VEGFR Inhibitors)
| Cat.No. | 제품명 | 정보 | 제품 사용 인용 | 제품 검증 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2842 | SAR131675 | SAR131675는 세포 유리 분석에서 IC50/Ki가 23 nM/12 nM인 VEGFR3 억제제로, VEGFR1/2보다 VEGFR3에 대해 약 50배 및 10배 더 선택적이며, Akt1, CDK, PLK1, EGFR, IGF-1R, c-Met, Flt2 등에는 활성이 거의 없습니다. |
|
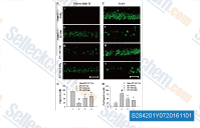
|
| S1010 | BIBF 1120 (Nintedanib) | Nintedanib은 VEGFR1/2/3, FGFR1/2/3 및 PDGFRα/β에 대한 강력한 삼중 혈관신생 키나제 억제제로, 세포 유리 분석에서 34 nM/13 nM/13 nM, 69 nM/37 nM/108 nM 및 59 nM/65 nM의 IC50를 가집니다. 3상. |
|
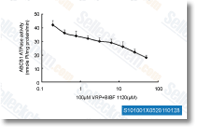
|
| S1119 | Cabozantinib (XL184) | IC50가 0.035 nM인 강력한 VEGFR2 저해제인 Cabozantinib (XL184)는 세포 유리 분석에서 c-Met, Ret, Kit, Flt-1/3/4, Tie2 및 AXL을 각각 1.3 nM, 4 nM, 4.6 nM, 12 nM/11.3 nM/6 nM, 14.3 nM 및 7 nM의 IC50로 저해합니다. 이는 AKT/GSK-3β/NF-κB 신호 전달 경로를 통해 결장암 세포에서 PUMA 의존성 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
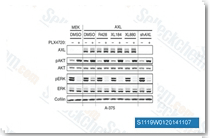
|
| S1164 | E7080 (Lenvatinib) | Lenvatinib은 VEGFR2(KDR)/VEGFR3(Flt-4)에 주로 작용하는 다중 표적 억제제로, IC50은 4 nM/5.2 nM이며, VEGFR1/Flt-1에 대해서는 덜 강력하고, 세포 없는 분석에서 FGFR1, PDGFRα/β에 비해 VEGFR2/3에 대해 약 10배 더 선택적입니다. Lenvatinib (E7080)은 또한 FGFR1-4, PDGFR, Kit (c-Kit), RET (c-RET)을 억제하며 강력한 항종양 활성을 보입니다. 3상. |
|
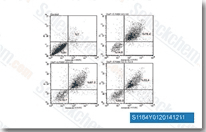
|
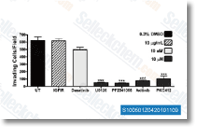
| S1005 | Axitinib (AG-013736) | Axitinib은 VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRβ 및 c-Kit의 다중 표적 억제제로, 돼지 대동맥 내피 세포에서 각각 0.1 nM, 0.2 nM, 0.1-0.3 nM, 1.6 nM 및 1.7 nM의 IC50을 가집니다. |
|
|
| S7667 | SU 5402 | SU5402는 VEGFR2, FGFR1 및 PDGF-Rβ에 대해 각각 20 nM, 30 nM 및 510 nM의 IC50를 갖는 강력한 다중 표적 수용체 Protein Tyrosine Kinase 억제제입니다. |
|

|
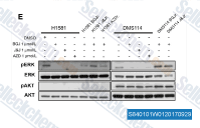
| S8401 | Erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493) | Erdafitinib은 잠재적인 항신생물 활성을 가진 강력하고 선택적인 경구 생체 이용 가능한 팬 fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 억제제입니다. 이 화합물은 또한 RET (c-RET), CSF-1R, PDGFR-α/PDGFR-β, FLT4, Kit (c-Kit) 및 VEGFR-2에 결합하여 세포 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
|
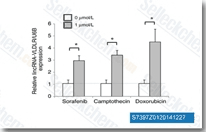
| S7397 | Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib은 세포 없는 분석에서 각각 6 nM 및 22 nM의 IC50을 갖는 Raf-1 및 B-Raf의 멀티키나아제 억제제입니다. Sorafenib은 VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 및 c-KIT를 각각 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM 및 68 nM의 IC50으로 억제합니다. Sorafenib은 Autophagy 및 Apoptosis를 유도하고 항암 활성과 함께 Ferroptosis를 활성화합니다. |
|
|
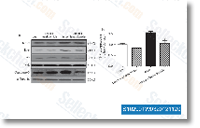
| S1029 | CC-5013 (Lenalidomide) | Lenalidomide는 PBMC에서 IC50이 13 nM인 TNF-α 분비 억제제입니다. Lenalidomide (CC-5013)는 ubiquitin E3 ligase cereblon (CRBN)의 리간드이며, CRBN-CRL4 ubiquitin ligase에 의해 두 가지 림프계 전사 인자인 IKZF1 및 IKZF3의 선택적 유비퀴틴화 및 분해를 유발합니다. Lenalidomide는 cleaved caspase-3 발현을 촉진하고 VEGF 발현을 억제하며 apoptosis를 유도합니다. |
|
|
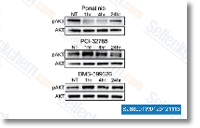
| S1490 | Ponatinib (AP24534) | Ponatinib은 Abl, PDGFRα, VEGFR2, FGFR1 및 Src의 새로운 강력한 다중 표적 억제제로, 무세포 분석에서 각각 0.37 nM, 1.1 nM, 1.5 nM, 2.2 nM 및 5.4 nM의 IC50을 가집니다. Ponatinib (AP24534)은 autophagy를 억제합니다. |
|
|
Solid tumors require the growth and dissemination of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels to support the metastatic growth of cancers. Following the recognition of growth factor receptor pathways that regulate angiogenesis, a number of small molecular inhibitors and antibodies have been developed that target the activity of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-VEGF receptor (VEGFR) pathway. This includes oral small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors currently in clinical practice, namely sunitinib and sorafenib. These are commonly used in the treatment algorithm for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), two indications that are known to develop resistance to conventional chemotherapeutics.
The VEGFs include five known structurally-related mammalian ligands (VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD, and placenta growth factor, PLGF). The VEGFs are disulfide-bonded homodimers, however, VEGFA and PLGF heterodimers are also known to exist. Due to alternative splicing or due to processing, VEGF ligands occur as several different variants. As a result, these variants bind differently to both VEGFRs and to co-receptors resulting in different biological responses including angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, permeability, inflammatory cell recruitment and fatty acid uptake. VEGFs are produced by several different cell types and act in a paracrine manner. The VEGFs bind to three structurally related tyrosine kinases (VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3). Modulating the effect of the VEGFRs are a number of co-receptors that lack intrinsic catalytic activity (i.e. heparin sulfate, neurophilins and integrins) and bind to VEGF.[1]
VEGFR1 (also known as Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, Flt1, in mice) is a single-transmembrane glycoprotein structurally related to VEGFR2 and VEGFR3. VEGFR1 is expressed at high levels in vascular endothelial cells, and along with VEGFR2 binds to VEGFA. VEGFR1 is noted to bind exclusively to VEGFB and PIGF. Expression of VEGFR1 is noted to occur during vessel growth and remodeling activity. Non-endothelial cells that express VEGFR1 includes monocytes and macrophages, human tropholblasts, renal mesangial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, dendritic cells and various tumor cells. A key regulator of VEGFR1 gene expression is hypoxia.[1]
VEGFR2 (also known as KDR; kinase insert domain receptor, in the human and Flk1; fetal liver kinase-1, in mice) binds VEGFA with a 10-fold lower affinity than VEGFR1. Other targets of VEGFR2 include proteolytically processed VEGFC and VEGFD. The only known ligand to uniquely bind to VEGFR2 is the open reading frame-encoded VEGFE. VEGFR2 is expressed in most adult vascular endothelial cells as well as circulating endothelial progenitor cells, pancreatic duct cells, retinal progenitor cells, megakaryocytes and hematopoietic cells. VEGFR2 expression is induced in conjunction with active angiogenesis (i.e. the uterus during the reproductive cycle) and in pathological process related to neovascularization (i.e. cancer). VEGFR2, often in combination with VEGFR3, is expressed at significantly upregulated levels in the tumor vascular endothelium in most common human solid tumors. Tumor cells can also express VEGFR2, however, epithelial and mesenchymal tumor cells typically express VEGFR1 rather than VEGFR2. Nevertheless, increased expression of VEGFR2 on tumor cells has been noted for melanoma and hematological malignancies. And, there is evidence supporting a relationship between chronic inflammation and tumor development.[1]
VEGFR3 (also known as Fms-like tyrosine kinase 4, Flt4 in the mouse) is activated by the binding of VEGFC or VEGFD, once these two ligands undergo proteolytic processing (this increases their affinity to VEGFR2 and VEGFR3). In addition, hVEGFD shows similar affinity to both VEGFR2 and VEGFR3, while mVEGFD binds only to VEGFR3. During embryogenesis, VEGFR3 expression occurs in the primary vascular plexus at day E8.5. In late stages of embryogenesis, VEGFR3 is expressed in venous endothelial cells of the cardinal vein, that results in VEGFR3-expressing lymphatics. Postnatally, VEGFR3 plays an important role in lymphatic endothelial cells, but its expression is also observed in endothelial cells engaged in active angiogenesis, such as tumor vessels, in endothelial tip cells of angiogenic sprouts in the developing retina or in chronic inflammatory wounds. The receptor is also found in non-endothelial cells such as osteoblasts, neuronal progenitors and macrophages – all of which may indirectly support angiogenesis. It remains unclear if tumor cells express VEGFR3. Despite this lack of clarity, inhibiting VEGFR3 activity is associated with the arrest of tumor vascularization, resulting in decreased vascular density in several tumor models.[1]
Since the VEGF-VEGFR pathway plays a significant role in angiogenesis, and it is widely known that VEGF is highly expressed in tumor and stromal cells, especially in the inflammatory cells of human tumors, dozens of angiogenesis inhibitors are currently undergoing clinical trials.[2] However, despite the number of compounds that has been identified for targeting the VEGF-VEGFR pathway, there is a high attrition rate. Several challenges in the development of angiogenesis inhibitors relate to their specificity, efficacy, side effects, and resistance to anti-angiogenic tumor therapy. However, the emergence of personalized medicine – based on the use of biomarkers – will likely lead to the identification of patient populations that is likely to define respondent groups.
