연구용
R788 (Fostamatinib) Disodium Syk 억제제
제품 번호S2206
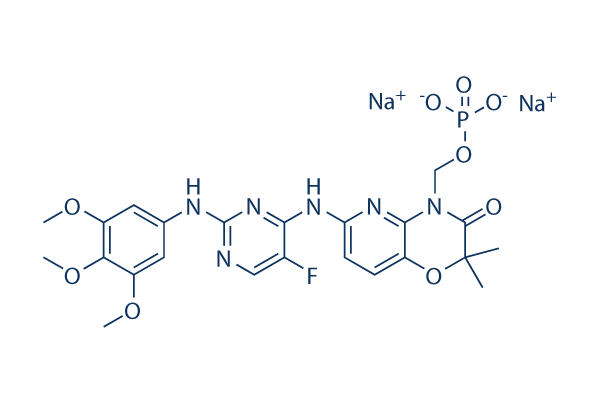
화학 구조
분자량: 624.42
품질 관리
세포 배양, 처리 및 작업 농도
| 세포주 | 분석 유형 | 농도 | 배양 시간 | 제형 | 활성 설명 | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramos | Function assay | Inhibition of SYK in human Ramos cells, IC50 = 0.267 μM. | 23350847 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| 클릭하여 더 많은 세포주 실험 데이터 보기 | ||||||
화학 정보, 보관 및 안정성
| 분자량 | 624.42 | 화학식 | C23H24FN6O9P.2Na |
보관 (수령일로부터) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS 번호 | 1025687-58-4 | SDF 다운로드 | 원액 보관 |
|
|
| 동의어 | Tamatinib Fosdium | Smiles | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
용해도
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 12 mg/mL
(19.21 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
몰농도 계산기
|
In vivo |
|||||
생체 내 제형 계산기 (투명한 용액)
1단계: 아래 정보 입력 (권장: 실험 중 손실을 고려하여 추가 동물 포함)
2단계: 생체 내 제형 입력 (이것은 계산기일 뿐 제형이 아닙니다. 용해도 섹션에 생체 내 제형이 없는 경우 먼저 당사에 문의하십시오.)
계산 결과:
작업 농도: mg/ml;
DMSO 원액 준비 방법: mg 약물 사전 용해 μL DMSO ( 원액 농도 mg/mL, 농도가 해당 약물 배치의 DMSO 용해도를 초과하는 경우 먼저 당사에 문의하십시오. )
생체 내 제형 준비 방법: 취하다 μL DMSO 원액, 다음 추가μL PEG300, 혼합하고 투명하게 한 다음 추가μL Tween 80, 혼합하고 투명하게 한 다음 추가 μL ddH2O, 혼합하고 투명하게 합니다.
생체 내 제형 준비 방법: 취하다 μL DMSO 원액, 다음 추가 μL 옥수수 기름, 혼합하고 투명하게 합니다.
참고: 1. 다음 용매를 추가하기 전에 액체가 투명한지 확인하십시오.
2. 용매를 순서대로 추가해야 합니다. 다음 용매를 추가하기 전에 이전 추가에서 얻은 용액이 투명한 용액인지 확인해야 합니다. 와동, 초음파 또는 뜨거운 물 중탕과 같은 물리적 방법을 사용하여 용해를 도울 수 있습니다.
작용 메커니즘
| 특징 |
Clinically used oral formulation of R406.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Syk
(Cell-free assay) 41 nM
|
| 시험관 내(In vitro) |
R935788은 R406의 메틸렌 인산염 전구약물로, 생체 내에서 R406으로 빠르게 전환될 수 있습니다. R406 (R935788의 시험관 내 활성 형태)은 33 nM에서 171 nM에 이르는 EC50 값으로 Syk 의존성 신호 전달을 선택적으로 억제하며, 다양한 세포에서 Syk 비의존성 경로보다 더 강력합니다. R406은 0.8 μM에서 8.1 μM에 이르는 EC50 값으로 다양한 미만성 거대 B세포 림프종 (DLBCL) 세포주의 세포 증식을 억제합니다. R406 처리는 BLNK, Akt, 글리코겐 신타제 키나아제-3 (GSK-3), 포크헤드 박스 O (FOXO) 및 ERK의 기저 인산화를 높은 (TCL-002) 세포뿐만 아니라 인산화된 Syk 수준이 낮은 (TCL1-551) 세포에서도 감소시킵니다. 또한, R406은 TCL1 백혈병에서 항-IgM 유도 Bcr 신호를 완전히 억제합니다. TCL1 백혈병에서 구성적으로 활성된 Syk 수준이 높음에도 불구하고, R406은 백혈병 세포에 선택적으로 세포독성을 나타내지 않습니다.
|
| 키나아제 분석 |
시험관 내 형광 편광 키나아제 분석
|
|
R406 (R935788의 시험관 내 활성 형태)은 DMSO에 연속적으로 희석된 후 키나아제 버퍼 (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/mL 아세틸화 BGG)에 1% DMSO로 희석됩니다. 키나아제 버퍼에 ATP와 기질을 실온에서 첨가하여 최종 DMSO 농도가 0.2%가 되도록 합니다. 키나아제 반응은 5 μM HS1 펩타이드 기질과 4 μM ATP를 포함하는 최종 부피 20 μL로 수행되며, 키나아제 버퍼에 0.125 ng의 Syk를 첨가하여 시작됩니다. 반응은 실온에서 40분 동안 진행됩니다. 반응은 FP 희석 버퍼에 희석된 EDTA/항-포스포티로신 항체 (최종 1×)/형광 포스포펩타이드 추적자 (최종 0.5×)를 포함하는 20 μL의 PTK 퀀치 믹스를 첨가하여 중지됩니다. 플레이트는 실온에서 어두운 곳에서 30분 동안 배양된 후 Polarion 형광 편광 플레이트 리더에서 판독됩니다. 데이터는 타이로신 키나아제 분석 키트에 제공된 포스포펩타이드 경쟁자와의 경쟁을 통해 생성된 보정 곡선을 사용하여 존재하는 포스포펩타이드의 양을 결정하도록 변환됩니다. IC50 결정을 위해 R406은 11가지 농도로 이중으로 테스트되며, Prism GraphPad 소프트웨어를 사용하여 비선형 회귀 분석을 통해 곡선 피팅이 수행됩니다.
|
|
| 생체 내(In vivo) |
마우스에서 R406의 혈장 반감기가 2시간 미만이라는 점을 고려할 때, R935788은 인간의 더 긴 혈장 반감기 (15시간)를 모방하여 각 치료 기간 동안 지속적인 Syk 억제를 제공하기 위해 3시간 간격으로 3회 분할 투여됩니다. 시험관 내에서 상대적으로 미미한 세포독성 효과에도 불구하고, R935788은 생체 내에서 백혈병 세포의 증식 및 생존을 유의하게 억제하며, 이는 구성적인 Syk 활성 억제보다는 항원 의존성 B 세포 수용체 (Bcr) 신호 전달 차단과 관련이 있습니다. 80 mg/kg/일로 18-21일 동안 R935788을 투여한 마우스는 치료 마지막 날 백혈병 CD5+/B220+ 세포가 검출되지 않는 상태에서 TCL1-002, TCL1-551 및 TCL1-870의 종양 성장을 강력하게 억제하고, 처리된 마우스의 생존 기간을 45/46일에서 170/172일로 중앙값 생존 기간이 유의하게 증가시키며, 6개월 추적 관찰 후 정상 B 림프구 생산에 영향을 미치지 않고 상당수의 마우스에서 악성 세포를 완전히 제거합니다. R935788 치료는 또한 비장과 림프절에서 말초 혈액으로 정상 및 악성 B 세포의 초기 및 일시적인 이동을 유도하며, 이는 이어서 악성 B 세포 집단의 선택적 성장 억제로 이어집니다. 또한, R935788은 Eμ-TCL1 형질전환 마우스에서 자발적으로 발생하는 TCL1 백혈병에 대해서도 효과적입니다.
|
참조 |
|
적용 분야
| 방법 | 바이오마커 | 이미지 | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-JAK2 / JAK2 / p-SRC / SRC / p-FAK / FAK / p-SYK / SYK / p-ERK / ERK p-SYK(525-526) / t-SYK / p-SYK(323) / p-BTK / t-BTK p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-AKT / AKT |

|
29340070 |
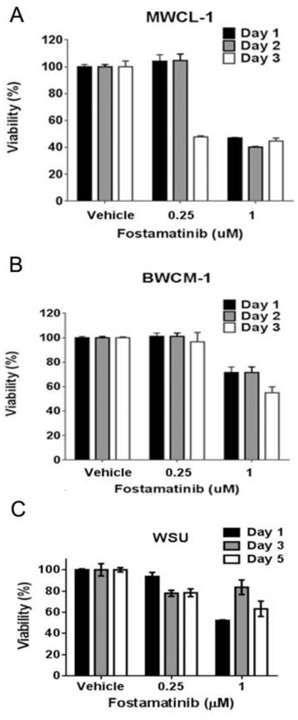
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
25748087 |
임상시험 정보
(데이터 출처 https://clinicaltrials.gov, 업데이트 날짜 2024-05-22)
| NCT 번호 | 모집 | 조건 | 스폰서/협력자 | 시작일 | 단계 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Sickle Cell Disease|Hb-SS Disease|Hemoglobin S|Disease Sickle Cell Anemia|Sickle Cell Disorders|Hemoglobin Beta Thalassemia Disease |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Immune Mediated Anemia|Immune Mediated Thrombocytopenia|Chronic GVHD |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06071520 | Completed | Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Fundación Pública Andaluza para la gestión de la Investigación en Sevilla |
March 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05613296 | Not yet recruiting | ITP - Immune Thrombocytopenia|Chronic ITP|Refractory ITP |
Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell''Adulto |
February 2023 | -- |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Myelofibrosis|Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine|Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 3 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04904276 | Terminated | ITP|Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 18 2021 | -- |
기술 지원
자주 묻는 질문
질문 1:
What’s the difference between S2625 and S2206?
답변:
The differences between S2625 and S2206: 1. S2206 is more stable than S2625; 2. The water solubility of S2206 is better than S2625; 3. The absorption of S2206 is harder than S2625, so you need to test the suitable dosage if you use it in animal assays; 4. The potency of S2206 and S2625 is similar.
